QDay: The World's First Quantum-Resistant EVM-Compatible Layer 2
Abstract: QDay is the world's first quantum-resistant, EVM-compatible Layer 2 network, designed to enhance blockchain security with quantum-resistant algorithms while maintaining compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
QDay represents a groundbreaking advancement in blockchain technology, offering the first quantum-resistant, EVM-compatible Layer 2 solution. Through its innovative two-phase implementation strategy, QDay addresses the critical challenge of quantum computing threats while preserving the practical advantages of existing blockchain infrastructure.
Adopting a comprehensive ecosystem approach, QDay integrates core DeFi applications and cross-chain bridges, delivering a complete quantum-resistant solution for the blockchain environment. The platform's token economic model ensures long-term sustainability while driving broad network participation.
QDay's roadmap from 2024 to 2026 provides a clear path for full implementation, integrating the platform's innovative technological features and positioning QDay as a pioneer in quantum-resistant blockchain technology.
1. Introduction
In the dynamic realm of blockchain technology, the persistent pursuit of enhanced security, scalability, and interoperability is paramount. The rise of quantum computing presents an existential threat to the cryptographic bedrock of current blockchain infrastructures. In response to this impending quantum revolution, we proudly present QDay, the first-of-its-kind post-quantum EVM-compatible Layer 2 network, built atop the pioneering quantum-resistant Abelian Blockchain (Layer 1). QDay is a testament to our commitment to fortify blockchain against quantum threats while elevating its performance and functionality.
1.1. The Synergy of Layer 2 and Quantum-Resistant Foundations
QDay is not merely an extension; it's a symbiotic enhancement of the Abelian Blockchain, the world's inaugural quantum-resistant blockchain platform. By leveraging the quantum-resistant algorithms already operational on Abelian, QDay fortifies the security measures to an unprecedented level. As a Layer 2 solution, it operates above the Abelian Blockchain, streamlining transaction processing, reducing costs, and accelerating confirmation times---all while inheriting the quantum-resistant properties of its Layer 1 counterpart.
1.2. Innovating with a POS-over-POW Model
Breaking new ground, QDay introduces an innovative consensus mechanism strategy by implementing a Proof of Stake (POS) model over the Abelian Blockchain's Proof of Work (POW) system. This novel POS-over-POW relationship is a first in the industry, offering the combined benefits of both systems: the robust security and decentralization of POW with the energy efficiency and scalability of POS. This strategic fusion ensures that QDay is not only quantum-resistant but also environmentally sustainable and poised for future growth.
1.3. QDay's Quantum-Resistant EVM-Compatible Layer 2: Core Advantages
Quantum-Resistant Security: Building on the quantum-resistant algorithms of the Abelian Blockchain, QDay introduces an additional layer of security, shielding the network against the quantum threat while maintaining the integrity and safety of user assets and data.
Enhanced Scalability: QDay's Layer 2 solution leverages the robust foundation of Abelian to significantly advance transaction throughput, aiming to achieve 1,000 TPS at inception, thus ensuring a scalable network ready to accommodate the ever-growing demands of blockchain applications.
Cost-Effective Transactions: By processing transactions off-chain and utilizing the POS consensus mechanism, QDay significantly reduces transaction fees, making blockchain technology more accessible and affordable for a diverse range of applications and users.
Accelerated Transaction Confirmations: QDay's network is engineered for speed, providing near-instantaneous transaction finality, which is crucial for applications that depend on quick and reliable transaction processing.
A Developer's Playground: With EVM compatibility at its core, developers can effortlessly transition to QDay using their preferred Ethereum-based development tools and languages, promoting innovation and streamlining the development process.
Interoperability as a Priority: QDay is meticulously crafted to ensure seamless interaction with other blockchain networks, promoting cross-chain transactions and contributing to a more cohesive and versatile blockchain ecosystem.
1.4. The Road Ahead: Pioneering the Future of Quantum-Resistant Blockchain
The development of quantum-resistant security in QDay will be conducted in two major phases:
Phase 1: L1-Assisted Quantum-Resistant Rollups with EVM Compatibility - In this phase, QDay will implement a quantum-resistant ledger by integrating ZK Rollups with the Abelian Blockchain, preserving EVM compatibility through the adoption of the account model and smart contract functionalities.This will allow for a smooth transition for Ethereum developers and enable the use of existing Ethereum tools and languages. With such L1-assisted quantum-resistant rollups, QDay will be resistant to quantum attacks targeting the modification of ledger data such as transaction orders, amounts, and state structure.In addition, when any attacks are detected, QDay will be able to prevent the loss of funds by temporarily halting the execution of rollups in a quantum-resistant manner, i.e., attackers cannot move forward once the rollups have been halted because they are not able to forge the quantum-resistant signatures generated by the rollup operators.
Phase 2: L2-Native Quantum-Resistant Accounts and Smart Contracts - In this phase, QDay will introduce quantum-resistant accounts by adding new secure keys to existing accounts and enabling operations that require these keys. To make this possible, QDay's EVM will be updated to support post-quantum cryptographic keys and algorithms. QDay will also support two types of smart contracts: traditional and quantum-resistant. Wallets that already work with EVM smart contracts can still use traditional contracts, while quantum-resistant contracts will only work with wallets that support QDay's advanced security features.
The two quantum-resistant mechanisms work independently but complement each other. The first defends ledger data from quantum attacks, while the second protects individual accounts. Together, they provide strong, comprehensive security for QDay. For example, even if an attacker steals private keys (by hacking a computer or other means), funds can still be protected by halting rollups, freezing affected accounts, and then resuming rollups. These actions are based on the consensus of rollup operators, ensuring the process remains decentralized and secure against quantum threats.

2. Technical Overview
2.1. Quantum-Resistant Cryptography in Abelian (Layer 1)
Abelian serves as the foundational Phase 0 of the QDay implementation. Its proven track record of successful operation over the years establishes a strong and solid foundation for QDay.
The Abelian blockchain employs quantum-resistant keys and algorithms to ensure the system's security against the advent of quantum computers. By utilizing lattice-based quantum-resistant assumptions such as Learning With Errors (LWE) and Ring-LWE, Abelian ensures strong protection against quantum attacks.These algorithms provide a robust foundation for the blockchain, ensuring that transactions and user data remain secure even in the face of future quantum computing advancements.
Security: Lattice-based cryptography offers enhanced security by resisting both classical and quantum attacks. This ensures the Abelian blockchain remains resilient against future quantum threats, protecting the integrity and confidentiality of user data and transactions.
Efficiency: These algorithms are optimized for performance, enabling secure and efficient transaction processing. Leveraging lattice-based cryptographic techniques, Abelian ensures the network handles a high volume of transactions without compromising speed or security.
Scalability: The scalability of lattice-based techniques enables the network to grow while maintaining security and efficiency. This positions Abelian to support a growing user base, fostering broader adoption and usage.
Future-Proofing: Abelian is dedicated to advancing quantum-resistant technologies through continuous research and development. The network will regularly update its cryptographic algorithms to strengthen security and performance, maintaining its leadership in quantum-resistant blockchain innovation.
2.2. Quantum-Resistant Cryptography in QDay-to-Abelian Rollups (Layer 2 to Layer 1)
This is the Phase 1 of QDay implementation.
Innovative POS-over-POW Consensus Integration
POS-over-POW is an innovative consensus mechanism that combines the strengths of both Proof of Stake (POS) and Proof of Work (POW) to create a more secure and efficient blockchain network. This hybrid approach leverages the established security of POW while introducing the energy efficiency and scalability of POS.
In a POS-over-POW system, the underlying blockchain operates on a POW consensus mechanism, which is known for its robustness and security. POW involves miners competing to solve complex mathematical puzzles, thereby validating transactions and securing the network. This process is computationally intensive and energy-demanding, but it delivers a high level of security because of the immense computational power required to compromise the network.
Building on the POW foundation, a POS layer is implemented. In POS, validators are selected to create new blocks and validate transactions based on the number of coins they hold and stake as collateral. This process is far less energy-intensive than POW, as it eliminates the need for solving complex puzzles, relying instead on economic incentives to encourage honest behavior from validators.
The POS-over-POW consensus mechanism offers several advantages over a pure POS-over-POS system:
Enhanced Security:
POW Foundation: Provides strong security through computational difficulty, making attacks both costly and challenging.
Synergistic Security: Combines the strengths of POS and POS, to enhance overall network security.
Energy Efficiency:
Reduced Energy Consumption: POS layer significantly lowers energy use compared to using POW alone.
Optimized Resource Usage: Balances security and energy efficiency by leveraging POW for security and POS for validation.
Scalability:
Improved Throughput: POS layer processes transactions more efficiently, enhancing scalability.
Layered Architecture: Allows modular upgrades, enabling continuous scalability improvements.
Economic Incentives:
Balanced Incentive Structure: Rewards both miners and validators, promoting active participation through POS incentives.
Stakeholder Engagement: Involves a broad range of participants, enhancing decentralization and resilience.
Resistance to Centralization:
Distributed Security: POW layer ensures decentralization by distributing security across a wide network of miners.
Mitigation of Centralization Risks: Reduces the risk of centralization found in pure POS systems by combining computational requirements with staked coins.
QDay's implementation of POS-over-POW leverages the robust security of the Abelian blockchain's POW foundation while integrating a POS layer to enhance scalability and efficiency.
Quantum-Resistant Rollups
The objective of quantum-resistant rollups is to ensure that QDay's ledger data cannot be altered or forged, even by attackers using quantum computers. If an attack is detected, QDay can securely halt rollup execution, preventing attackers from proceeding since they cannot forge the quantum-resistant signatures generated by rollup operators. During this halt, affected accounts can be frozen, and authorities notified, with rollup execution resuming once corrective measures are in place. Unlike QDay, existing Layer 2 solutions lack this capability, as they cannot stop quantum attackers from cracking the private keys of rollup operators.
QDay's implementation of quantum-resistant rollups is designed for simplicity. Each rollup operator uses an account on the Abelian Blockchain, with rollup data secured by quantum-resistant keys and algorithms native to the Layer 1. Beyond leveraging this quantum-resistant foundation, the rest of the rollup implementation functions similarly to other Layer 2 solutions. Specifically, QDay adapts Polygon's ZK Rollups to integrate with the unique features of the Abelian Blockchain. The technical details will be covered in the next section.
2.3. Quantum-Resistant Accounts and Smart Contracts in QDay (Layer 2)
This is the Phase 2 of QDay implementation.
QDay aims to deliver quantum-resistant security equal to or greater than its Layer 1 foundation, while maintaining EVM compatibility, high transaction speed, and low latency. To achieve this, QDay will implement its own quantum-resistant accounts and smart contracts, separate from the Layer 1 and rollups. This approach ensures QDay becomes fully quantum-resistant while still benefiting from the added security of quantum-resistant rollups.
Implementing Phase 2 will be complex, as it involves redesigning QDay's EVM to support quantum-resistant keys and algorithms while remaining compatible with existing keys and smart contracts. To manage this, QDay will introduce two transaction modes: legacy transaction and quantum-resistant transaction.
Legacy Transaction
Legacy transactions refer to the existing transaction format supported by the current EVM implementation in QDay validator nodes, distinguishing them from quantum-resistant transactions. Legacy transactions are supported in the following two cases:
Accounts using legacy keys to interact with the legacy smart contracts.
Accounts using legacy keys to interact with the quantum-resistant smart contracts that include a fallback mechanism to support legacy keys.
In the second case, the account does not need to know whether the smart contract supports quantum-resistant keys and algorithms. The fallback mechanism is seamless and transparent to users, meaning third-party wallets without quantum-resistant key support can still interact with these quantum-resistant smart contracts.
However, allowing quantum-resistant keys to interact with legacy (non-quantum-resistant) smart contracts is less meaningful. This so-called backward compatibility is not recommended due to security concerns.
Quantum-Resistant Transaction
Quantum-resistant transactions are handled by the upgraded EVM implementation in QDay validator nodes, which supports quantum-resistant keys and algorithms. These transactions are only supported in the following scenario:
- Accounts using quantum-resistant keys to interact with the quantum-resistant smart contracts.
In other words, quantum-resistant transactions are entirely independent of legacy keys. Only wallets equipped with quantum-resistant key and algorithm support can initiate these transactions. To successfully complete Phase 2, QDay will provide a reference implementation of quantum-resistant wallets as a core component. The design and implementation details of these wallets will be published in a separate whitepaper.
3. Tokenomics
The total supply of QDAY is 22,517,998,100, mirroring the total supply of ABEL. The distribution of QDAY is designed to ensure network security, incentivize participation, and foster community growth. The QDay DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) will be responsible for the allocation of QDAY after TGE (Token Generation Event).
3.1 Token Distribution
| Category | % | Amount (100M) | Lock Up | Vesting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Validators | 50% | 112.59 | ||
| Community Growth | 4.5% | 10.13 | ||
| Initial Liquidity | 0.5% | 1.13 | ||
| Investors | 10% | 22.52 | 24 months | 12 months |
| ABEL Staking Airdrop | 10% | 22.52 | 48 months | |
| Team | 15% | 33.78 | 48 months | 24 months |
| Insurance Fund | 10% | 22.52 | Till DAO decides | |
| Total | 100% | 225.18 |
All QDAY tokens will be generated at the TGE, with distribution following the allocation outlined in the above table. Lock-up and vesting rules will be enforced either through smart contracts deployed on QDay or under the supervision of the DAO.
Validators - The majority of QDAY (50%) will be allocated to validators. The validators will be responsible for running the QDay validator nodes and securing the network. Rewards will be calculated daily based on the validators' online time during that period and distributed every four weeks. To be eligible to operate as a validator, the following requirements must be met:
The party must be a legal entity or an individual who is at least 20 years old.
The party must either (1) operate a validator node securely and reliably, or (2) delegate validator operations to a capable third party.
The party must agree to adhere to the governance and consensus rules established by the QDay DAO.
The party must stake a minimum of 100,000 QDAY to the validator node. The initial QDAY can be obtained either by staking ABEL to get the airdrop or by purchasing it from the market.
Community Growth - 4.5% of QDAY will be allocated to incentivize community initiatives, marketing, grants, partnerships, and related activities. Distribution will be managed by QDay DAO, based on contributions to the QDay ecosystem. To ensure long-term community incentives, this portion of QDAY will be distributed gradually over 12 to 48 months.
Initial Liquidity - 0.5% of QDAY will be allocated to establish initial liquidity pools for QDAY trading pairs on decentralized exchanges (DEX). This will help generate a market price shortly after the TGE, which is essential for the proper functioning of all QDAY-related DeFi dApps.
Investors - 10% of QDAY will be allocated to strategic investors committed to supporting QDay in the long term. These tokens will be locked for 24 months post-investment and will then be gradually distributed over a 12-month period.
ABEL Staking Airdrop - 10% of QDAY will be allocated as an airdrop to ABEL stakers, specifically rewarding long-term supporters of Abelian. By participating in ABEL staking on QDay, stakers will receive a portion of QDAY as rewards. The airdrop will occur immediately after staking, with the received QDAY automatically staked to a validator node selected by the staker. During the 48-month lock-up period for the airdropped QDAY, stakers will continue earning QDAY rewards from validator operations.
Team - 15% of QDAY will be allocated to the team members. The tokens will be locked for 48 months and will be distributed gradually over a period of 24 months. The longest lock-up period of this portion of QDAY is to ensure the team members are committed to the long-term success of QDay.
Insurance Fund - 10% of QDAY will be reserved to cover potential fund losses in officially recognized cases, such as hacks or validator misconduct. Given QDay's robust security, the likelihood of such incidents is extremely low. As a result, the insurance fund is not expected to be used and will remain permanently locked if no losses occur.
4. Phase 1: L1-Assisted Quantum-Resistant Rollups with EVM Compatibility
In Phase 1, QDay will introduce a quantum-resistant ledger by integrating ZK Rollups into the Abelian Blockchain while maintaining compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). This ensures a seamless transition for Ethereum developers, enabling them to use existing tools, languages, and the familiar account and smart contract model of the EVM.The L1-assisted quantum-resistant rollups will protect QDay from quantum attacks that aim to alter ledger data, such as transaction orders, amounts, and state structures. In addition, if an attack is detected, QDay can prevent fund losses by temporarily halting rollup execution in a quantum-resistant manner. Once halted, attackers cannot proceed because they are unable to forge the quantum-resistant signatures generated by the rollup operators. This section will focus on the technical details of the quantum-resistant rollups in QDay.
4.1. Introduction to ZK Rollups
ZK Rollups, or Zero-Knowledge Rollups, are an advanced Layer 2 scaling solution designed to overcome blockchain limitations, particularly in scalability and transaction throughput. They work by aggregating multiple transactions into a single batch and submitting it to the Layer 1 blockchain. This approach significantly reduces the computational load and storage demands on the main chain, enabling faster and more efficient processing.
The core innovation of ZK Rollups lies in their use of zero-knowledge proofs, a cryptographic technique that allows one party to prove the validity of a statement without revealing any details about the statement itself. In the context of ZK Rollups, this enables transactions to be verified for accuracy without exposing the underlying transaction data. This approach not only enhances privacy but also ensures a secure and efficient verification process.
ZK Rollups also present an effective solution to the scalability trilemma, which asserts that achieving decentralization, security, and scalability simultaneously is inherently difficult. By shifting transaction processing to Layer 2 while retaining the robust security guarantees of Layer 1, ZK Rollups achieve a balanced approach that improves network performance without sacrificing decentralization or security.
4.2. QDay's Adoption of Polygon ZK Rollups Technology
QDay's adoption of Polygon ZK Rollups technology is a strategic step toward utilizing one of the most advanced and reliable Layer 2 solutions available. Built on strong cryptographic foundations, Polygon ZK Rollups are engineered to efficiently process high transaction volumes. This aligns perfectly with QDay's goals of achieving greater scalability and enhanced privacy.
Polygon's ZK Rollups utilize zk-SNARKs (Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Arguments of Knowledge), a highly efficient form of zero-knowledge proof. These proofs are compact and can be verified quickly without requiring multiple interactions between the prover and verifier. This efficiency makes zk-SNARKs especially well-suited for blockchain applications, where speed and scalability are paramount.
In practice, QDay leverages Polygon ZK Rollups to process transactions off-chain, significantly reducing the load on the Abelian main chain. Multiple transactions are aggregated into a single proof, which is submitted to the Abelian chain for finalization. This method enhances transaction throughput, lowers gas fees, and makes the network more cost-effective for users.
Moreover, Polygon's ZK Rollups are built for high interoperability, enabling smooth integration with diverse blockchain ecosystems. This adaptability is essential for QDay, as it seeks to deliver a scalable and flexible Layer 2 solution capable of evolving alongside the blockchain industry's changing demands.
Polygon's ZK Rollups are built for high interoperability, enabling smooth integration with diverse blockchain ecosystems. This adaptability is essential for QDay, as it seeks to deliver a scalable and flexible Layer 2 solution capable of evolving alongside the blockchain industry's changing demands.
A distinctive feature of QDay's implementation is its use of Abelian, a blockchain akin to Bitcoin, as the Layer 1 foundation for its ZK Rollups. This approach diverges from the conventional use of EVM-compatible chains as the Layer 1 base. As a result, substantial modifications to the standard Polygon ZK Rollups framework are required to ensure compatibility with Abelian's architecture.
Abelian, like Bitcoin, employs a distinct consensus mechanism and transaction model compared to EVM-compatible chains. While EVM-compatible chains rely on an account-based model, Abelian operates on a UTXO (Unspent Transaction Output) model. This fundamental difference requires reengineering the ZK Rollups' data structures and proof generation mechanisms to align with the UTXO model.
In addition, Abelian's quantum-resistant consensus algorithm must be incorporated into the rollup's verification process. This requires modifying the proof submission and verification protocols to align with Abelian's consensus rules. While the specifics of these modifications are complex, the primary objective is to ensure seamless integration between the rollup and the Abelian main chain, preserving the security and efficiency advantages of both layers.
4.3. Benefits of Quantum-Resistant Rollups
Quantum-resistant rollups offer a key advantage: they ensure that ledger data is quantum-proof once the rollups are confirmed by the Abelian blockchain. This security extends to both confirmed and pending data - transactions submitted to QDay but not yet finalized by Abelian - protecting against 51% attacks even with access to a quantum computer.
A groundbreaking feature of QDay is its ability to halt rollup execution in a quantum-resistant manner. Attackers cannot proceed once a rollup is halted, as they are unable to forge the quantum-resistant signatures generated by rollup operators. Importantly, this halt mechanism operates solely on the rollup layer and does not interfere with the functioning of the QDay blockchain itself.
As this feature is not supported by any existing Layer 2 solution, we will demonstrate its functionality with a concrete example.
The following events are set to take place in the timeline:
An attacker with access to a quantum computer exploits a vulnerability in a DeFi dApp on QDay, draining all funds from the pool in a rug pull.
The stolen funds are transferred to a QDay account under the attacker's control.
A user notices the rugpull and reports the incident to the dApp provider.
The dApp provider freezes the attacker's account and escalates the incident to QDay DAO.
The QDay DAO initiates a vote proposal to halt rollup execution for 12 hours.
All DAO members are prompted to vote on the proposal within 30 minutes.
The vote passes and the rollups execution is halted immediately. From this point onwards, the attacker is unable to transfer the funds out of QDay since the QDay Bridge only processes transactions that have been confirmed by rollups.
The dApp provider is notified that they have approximately 12 hours to take necessary actions to secure users' funds. If additional time is required, they can request an extension of the suspension period from the QDay DAO.
The dApp provider contacts the token issuer to freeze all addresses controlled by the attacker. Notably, this freeze operation is executed as a smart contract call on QDay and is unaffected by the rollup halt.
The token issuer requests solid evidence of the rugpull from the dApp provider. In this example, the dApp provider submits the required evidence, which successfully passes the token issuer's review.
The token issuer freezes the attacker's addresses.
The rollups execution is resumed either: (1) after 12 hours, or (2) the dApp provider notifies the QDay DAO that all required actions have been taken and the rollups execution can resume In the latter case, the QDay DAO will also vote on a proposal to resume the rollups execution.
The QDay Blockchain returns to normal operation. The dApp provider reports the rug pull to the police or other relevant authorities, initiating further legal actions against the attacker.
If additional actions are required, the QDay DAO will vote on the relevant proposals. Typically, such actions are initiated based on recommendations from the police or other relevant authorities.
It is worth noting that the above example assumes the attacker has access to a quantum computer. Despite this, the attacker cannot transfer funds out of QDay via the QDay Bridge, as the rollup process depends on quantum-resistant signatures generated by rollup operators. This example demonstrates how the quantum-resistant halt mechanism significantly enhances the security of dApps deployed on QDay.
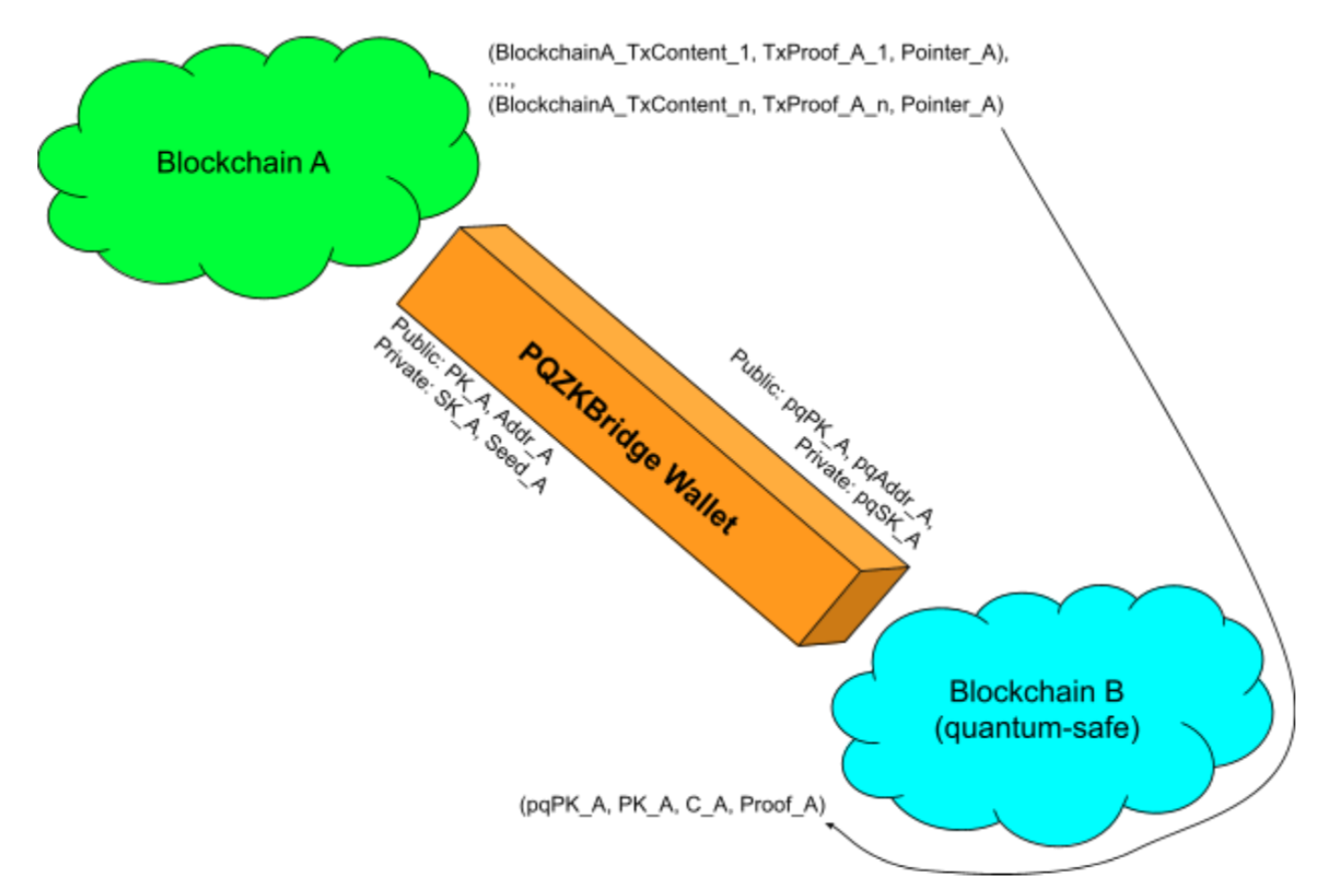
4.4. Future Work: PQZK Bridge
What is PQZK Bridge?
The PQZK Bridge, or Post-Quantum Zero-Knowledge Bridge, is a cryptographic protocol designed to securely and efficiently transition blockchain systems to post-quantum security standards. By integrating zero-knowledge proofs with post-quantum cryptographic algorithms, it establishes a resilient framework capable of withstanding the advanced capabilities of quantum computers.
Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) enable one party to prove the truth of a statement to another without disclosing any details about the statement itself. In blockchain, ZKPs allow transactions to be verified for accuracy while preserving privacy. Post-quantum cryptography (PQC), on the other hand, focuses on cryptographic algorithms designed to withstand attacks from quantum computers.
The PQZK Bridge integrates these two technologies by using post-quantum cryptographic primitives to construct zero-knowledge proofs. This ensures that the proofs remain secure even in the presence of quantum adversaries. The PQZK Bridge acts as a middleware layer that facilitates the deployment of PQZK Rollups on existing blockchain platforms, providing a seamless upgrade path to quantum security.
 Implementing QDay's PQZK Rollups with PQZK Bridge
Implementing QDay's PQZK Rollups with PQZK Bridge
To implement PQZK Rollups, QDay will leverage the PQZK Bridge to transition from traditional ZK Rollups to a fully quantum-resistant solution. Here's how this process will be achieved:
Integration of Post-Quantum Cryptographic Primitives: The first step involves integrating post-quantum cryptographic primitives into the rollup framework. These primitives, such as lattice-based cryptography or hash-based signatures, replace traditional cryptographic algorithms used in zero-knowledge proofs.
Construction of PQZK Proofs: With these post-quantum primitives, QDay will construct PQZK proofs. These proofs will preserve the zero-knowledge property, enabling transaction verification without exposing sensitive information, while also providing resistance against quantum attacks.
Modification of Rollup Protocols: The rollup protocols will be updated to integrate PQZK proofs, requiring modifications to the processes for proof generation, submission, and verification to accommodate the new post-quantum cryptographic constructs.
Deployment on Abelian Layer 1: The updated rollup protocols, now incorporating PQZK proofs, will be deployed on the Abelian Layer 1 blockchain. Abelian's quantum-resistant properties will complement the PQZK Rollups, providing a robust, end-to-end solution resistant to quantum attacks.
Testing and Optimization: Extensive testing will be carried out to verify the functionality and efficiency of the PQZK Rollups. Optimization efforts will focus on minimizing the computational overhead associated with post-quantum cryptographic operations, ensuring that the rollup solution remains scalable and performant.
Extending PQZK Rollups to Other EVM-Compatible Chains
The advantages of PQZK Rollups extend beyond QDay and Abelian. The PQZK Bridge technology can be adapted for other EVM-compatible chains, enabling them to achieve quantum security. Here's how this can be achieved:
Adapting PQZK Bridge for EVM-Compatible Chains: The PQZK Bridge can be customized to integrate with the unique architectures and consensus mechanisms of EVM-compatible chains. This involves modifying the bridge protocols to ensure compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and other related technologies.
Deployment of PQZK Rollups on EVM-Compatible Chains: After adaptation, the PQZK Bridge can facilitate the deployment of PQZK Rollups on various EVM-compatible chains. This enables these chains to process transactions off-chain in a quantum-resistant manner, enhancing their scalability and security.
Interoperability and Ecosystem Integration: The interoperability features of the PQZK Bridge enable seamless integration of PQZK Rollups across different blockchain ecosystems. This promotes a more secure and interconnected blockchain landscape, allowing multiple chains to benefit from quantum-resistant transaction processing.
Community and Developer Support: To support the adoption of PQZK Rollups, comprehensive documentation, developer tools, and community resources will be made available. These resources will enable blockchain developers to efficiently implement and deploy PQZK Rollups on their platforms, accelerating the shift toward quantum-secure blockchain technology.
By adopting PQZK Rollups through the PQZK Bridge, QDay strengthens its own security while enhancing the resilience of the broader blockchain ecosystem against quantum threats. This forward-thinking approach ensures that blockchain systems remain secure, scalable, and efficient as quantum computing technology continues to advance.
5. Phase 2: Quantum-Resistant Account with EVM Compatibility
In Phase 2, QDay will introduce a quantum-resistant account and legacy account, along with the following related concepts:
quantum-resistant wallets and legacy wallets;
quantum-resistant contracts and legacy contracts;
quantum-resistant dApps and legacy dApps.
Each mnemonic phrase from a legacy account can seamlessly derive a corresponding quantum-resistant account, ensuring an easy transition for users. This design allows users to access both account types using the same mnemonic phrase. EVM-compatible wallets will continue to function with legacy accounts without any changes, remaining unaware of quantum-resistant accounts. In contrast, quantum-resistant wallets will support both legacy and quantum-resistant accounts under the same mnemonic phrase. To facilitate adoption, QDay will provide an open-source reference implementation of the quantum-resistant wallet, promoting transparency and ease of integration.
Apart from sharing the same mnemonic phrase, the quantum-resistant account is completely independent from the legacy account. This is deliberately designed to ensure the post-quantum security of the new account. Specifically, the following objectives will be achieved in Phase 2:
Legacy accounts will continue to function as before, fully supported by legacy wallets and legacy smart contracts.
Quantum-resistant accounts will be compatible with quantum-resistant wallets, while legacy wallets are not expected to support quantum-resistant accounts.
The QDay team's reference implementation of the quantum-resistant wallet will support the legacy accounts. For the quantum-resistant wallets implemented by third parties, supporting legacy accounts will be optional.
The quantum-resistant contracts will NOT support the legacy accounts. This is key to ensure that the post-quantum security will not be compromised by the use of non-quantum-resistant cryptographic primitives.
Quantum-resistant contracts will maintain compatibility with legacy contracts in two ways: 1) they can include legacy functions that are not quantum-resistant; 2) quantum-resistant functions can be accessed by legacy wallets through an external quantum-resistant signature generator.
Some quantum-resistant dApps may support the legacy accounts by implementing both quantum-resistant and legacy protocols.
Quantum-resistant accounts can interact with quantum-resistant smart contracts and dApps using the quantum-resistant wallets. They may interact with legacy smart contracts and dApps if quantum-resistant wallets include a fallback mechanism for these scenarios.
The table below shows whether a quantum-resistant object can interact with or support a legacy object. Since legacy objects cannot interact with quantum-resistant objects, the corresponding reverse table is not included.
| Object | Legacy Account | Legacy Wallet | Legacy Contract | Legacy dApp |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quantum-Resistant Account | may fallback to | cannot be used by | may interact with | may interact with |
| Quantum-Resistant Wallet | may support | same mnemonics | may support | may support |
| Quantum-Resistant Contract | not compatible | not compatible | not compatible | not compatible |
| Quantum-Resistant dApp | may support | may be used by | may support | may support |
To summarize, the objective of Phase 2 is to add the support for the quantum-resistant objects without compromising any post-quantum security features while maintaining the maximum backward compatibility with the legacy objects. The remainder of this section will outline the overall design of the core components in QDay Phase 2, followed by a detailed discussion of the design principles and trade-offs.
5.1. Quantum-Resistant Account
The quantum-resistant account in QDay will use the same post-quantum cryptographic primitives as in Abelian Blockchain. While it shares the same mnemonic phrase as the legacy account, it diverges completely in functionality and structure from that point forward.
The process of deriving the quantum-resistant account from a BIP-39 mnemonic phrase is defined in AIP-11 (Abelian Improvement Proposal 11). For the convenience of the readers, we will briefly describe the process here.
Step 1: From Mnemonic to Entropy-Seed: AIP-11 uses the same entropy-seed derivation process as in BIP-39. However, AIP-11 requires the entropy-seed to be 256 bits long which corresponds to 24 mnemonic words. To address this, for mnemonic phrases with less than 24 words, we will pad the mnemonic phrase with the word "abandon" (the first word in the BIP-39 wordlist) until it has 24 words while for mnemonic phrases with more than 24 words, we will truncate the mnemonic phrase to 24 words.
Step 2: From Entropy-Seed to Master-Seed: The entropy-seed is then used to derive the 512-bit master-seed using a deterministic key derivation function. The key derivation function is defined as follows:
MasterSeed=PRF(EntropySeed,'AccountMasterSeed')MasterSeed=PRF(EntropySeed,'AccountMasterSeed')where PRFPRF is a post-quantum key derivation function using KMAC256 as the underlying hash function, defined as follows:
PRF(𝑘𝑒𝑦,𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡):=KMAC256(𝑘𝑒𝑦,𝑖𝑛𝑝𝑢𝑡,512,'ABELIANPRF').Step 3: From Master-Seed to Account-Root-Seeds: In Abelian, each account consists of a set of root seeds, namely CoinSpKeyRootSeed, CoinSnKeyRootSeed, CoinDetectorRootKey and CoinVKRootSeed, collectively referred to as Account-Root-Seeds. All root seeds are 512 bits long, derived from the marster-seed by using the following key derivation functions:
Note that the PRF function is the same as the one used in the previous step.
Step 4: From Master-Seed to Public-Rands: In AIP-11, each set of root seeds can be used to derive multiple addresses corresponding to different values of public rand. In QDay, to conform to the convention of existing Hirachical Deterministic Wallets (HDW), we will use the following deterministic function defined by AIP-11 to derive an public rand from the master-seed and a sequence number. Specifically, the public rand is derived as follows:
where
Step 5: From Account-Root-Seeds and Public-Rand to Address and Private-Key: Once both the account-root-seeds and the public-rand are derived, the corresponding address and private-key can be derived deterministically. As this process is beyond the scope of AIP-11, we will use the same process implemented in the Abelian SDK v2 to gain more consistency with the ecosystem of the L1 chain.
5.2. Upgrade of QDay Nodes
To enable the functionality of quantum-resistant accounts, the blockchain must first support the transfer of the native token QDAY between legacy accounts and quantum-resistant accounts. This requires upgrading QDay nodes to: 1) recognize the new address format used by quantum-resistant accounts, 2) verify signatures generated by quantum-resistant accounts, and 3) facilitate the transfer of QDAY between legacy and quantum-resistant accounts. However, fulfilling the third requirement is not straightforward. This is because we must maintain backward compatibility, allowing legacy wallets to perform transfers without being aware of the new address format used by quantum-resistant accounts.
Challenge: Is it possible to support the transfer of the native token QDAY between the legacy account and the quantum-resistant account without changing the legacy wallets?
To overcome this challenge, we will develop a smart contract on the QDay Blockchain that serves as a bridge between legacy accounts and quantum-resistant accounts. This smart contract will be a legacy contract, ensuring compatibility with legacy wallets.The general process is as follows:
The legacy account invokes the send function of the smart , specifying the quantum-resistant account as the recipient and the amount of QDAY to be transferred as the input.
The smart contract verifies the signature of the legacy account and validates the recipient address.
The smart contract receives QDAY from the legacy account and transfers it to the quantum-resistant account.
In the last step, the smart contract transfers QDAY from its own legacy address to the recipient's quantum-resistant address. This is carried out by calling a new primitive function legacy_to_quantum_resistant_transfer implemented by QDay Node. The EVM implementation of QDay Node will be upgraded to support this primitive function along with another primitive function quantum_resistant_to_legacy_transfer which handles the reverse process.
Though the interface of the above two primitive functions looks simple, the implementation is non-trivial. It requires a comprehensive set of cryptographic operations involving both the legacy algorithms and the post-quantum ones. The technical details are beyond the scope of this whitepaper and will be elaborated when we open-source the QDay Node's implementation.
5.3. Quantum-Resistant Wallet
It is clear that all existing EVM-based wallets will not support the quantum-resistant account defined by QDay, as they are not designed to support post-quantum security features. Therefore, a new type of wallet is required to support QDay's quantum-resistant account. QDay will provide a reference implementation of this wallet in Phase 2, and the source code will be open-sourced to allow the community or other parties to build compatible quantum-resistant wallets.
To create or import a quantum-resistant account, the user will use the same mnemonic phrase as the legacy account. The wallet will derive the quantum-resistant account from the mnemonic phrase , enabling it to transfer the native token QDAY and interact with the quantum-resistant smart contracts and dApps.
To transfer QDAY from quantum-resistant account to legacy account, the quantum-resistant wallet will directly submit a transaction to the blockchain nodes. This differs from transferring QDAY from a legacy account to a quantum-resistant account using legacy wallets, as outlined in the previous section. After the Phase 2 upgrade, QDay nodes will be able to process such transactions directly, eliminating the need for the smart contract bridge in this case.
The main purpose of the quantum-resistant wallet is to interact with the quantum-resistant smart contracts and dApps. To understand how the quantum-resistant wallet interacts with these smart contracts, it's essential to first examine the design and implementation of the quantum-resistant smart contracts themselves. As such, we will cover this in the next section, where we provide a detailed explanation of the quantum-resistant smart contracts.
In the reference implementation, we will provide a fallback mechanism to support those scenarios. Specifically, to interact with a legacy smart contract, the wallet will use the corresponding legacy address to call the smart contract. The wallet will automatically handle the migration of assets. For example, when interacting with a smart contract that swaps QDAY for PQUSD, the wallet will first transfer the QDAY to the legacy address, execute the smart contract call, and then transfer the PQUSD to the quantum-resistant address once the transaction is complete.
5.4. Quantum-Resistant Contracts
In QDay Phase 2, a quantum-resistant contract can be considered as a legacy contract with an extra layer of post-quantum signature verification. From the caller's perspective, the quantum-resistant contract functions just like the legacy one. The only difference is that for each call to contract methods intended to be quantum-resistant, the caller must provide an extra quantum-resistant signature. This signature is passed as a standard parameter in the contract method and is verified by the contract itself.
Consider the transfer method in a quantum-resistant ERC20 contract. The legacy ERC20 method signature is as follows:
function transfer(address to, uint256 value) external returns (bool);The quantum-resistant version of the method is as follows:
function pq_transfer(bytes pq_sig_data, address to, uint256 value) external returns (bool);where pq_sig_data is the quantum-resistant signature.
As a convention defined by QDay, the function name must be prefixed with pq_ and the signature is enforced to be the first parameter. This convention makes it easy to distinguish the quantum-resistant methods from the legacy ones. More importantly, with this convention, the QDay nodes can verify the quantum-resistant signatures automatically without extra codes in the contract. Specifically, as long as the signature data is generated in the standard way defined by QDay and passed as the first parameter to a function of which the name is prefixed with [pq_]{.underline}, the QDay nodes will verify the signature using the built-in quantum-resistant signature verification mechanism.
Theoretically, the same mechanism can be implemented in a legacy contract on any EVM-compatible chain, provided the following issues are addressed:
The quantum-resistant signature can be generated by either a quantum-resistant wallet or an external tool conforming to the standard defined by QDay.
The quantum-resistant signature can be verified within the contract function using the regular EVM instructions.
The first issue is relatively straightforward to address, though it may result in a less-than-ideal user experience when using legacy wallets alongside an external tool. The second issue is more challenging, as implementing quantum-resistant cryptographic operations within the contract function using regular EVM instructions is complex. Also, since these operations are resource-intensive, they could lead to prohibitively high gas fees for users.
It's important to note that the second issue does not exist in QDay, as quantum-resistant signature verification is implemented as a built-in feature. The computation is handled natively on the operating system of the QDay nodes (rather than through the EVM), meaning the computational cost is not passed on to users in the form of gas fees.
5.5. Quantum-Resistant dApps
As seen above, smart contracts must be upgraded to support the quantum-resistant signatures. To ensure a smooth transition, dApps deployed in Phase 1 can take the following approach to gradually upgrade to the quantum-resistant ones:
Keep the user interface of the dApp unchanged. Legacy wallets can interact with the dApp as before.
Add new quantum-resistant methods to the smart contracts used by the dApp , while ensuring that all existing legacy methods must be kept unchanged.
Upgrade the user interface of the dApp to add support quantum-resistant wallets.
However, in some cases, it may be necessary to implement a separate quantum-resistant version of the dApp, without compatibility with legacy wallets, to ensure that the quantum-resistant contracts remain unaffected by legacy ones. It is important to note that QDay imposes no restrictions on when, how, or if dApps are upgraded to quantum-resistant versions - this decision is left entirely to the dApp developers.
5.6. The Design Principles
The design of QDay Phase 2 follows these core principles:
- Backward Compatibility
Legacy accounts and wallets continue to function without modification.
Legacy smart contracts remain fully operational.
Existing dApps can gradually transition to quantum-resistant versions.
- Security Isolation
Quantum-resistant accounts are completely independent from legacy accounts (sharing only the mnemonic phrase).
Quantum-resistant smart contracts cannot be compromised by legacy cryptographic primitives.
Clear separation between quantum-resistant and legacy transaction types.
- Seamless User Experience
Same mnemonic phrase can derive both legacy and quantum-resistant accounts.
Quantum-resistant wallets can optionally support legacy operations.
Automatic asset migration between legacy and quantum-resistant accounts when needed.
- Efficient Implementation
Quantum-resistant signature verification is integrated into QDay nodes.
Additional gas costs for quantum-resistant operations.
Standardized prefix (pq_) for quantum-resistant contract methods.
- Flexible Adoption
The developers of dApps can choose their own upgrade timeline.
Multiple implementation approaches available (gradual upgrade or complete replacement).
Optional fallback mechanisms for legacy compatibility.
- Clear Standards
Consistent naming conventions for quantum-resistant methods.
Standardized signature data format.
Well-defined interfaces between legacy and quantum-resistant components.
These principles ensure that QDay can smoothly transition to quantum-resistant security while preserving usability and supporting organic ecosystem growth.
6. Application Ecosystem
According to the features described in the previous sections, the QDay application ecosystem will be composed of the following categories:
Category 1: Application related to Abelian
Since Abelian serves as the core foundation for QDay's security, especially in Phase 1 where the post-quantum features of the L2 chain are fully derived from the rollups to the L1 chain, applications related to Abelian will be the first to be launched on QDay. Due to the complexities of managing both L1 and L2 chains, all early-stage applications related to Abelian on QDay are expected to be developed by either the QDay team or the Abelian team.Currently, the main applications fall in this category are Wrapped ABEL (wABEL) and Abelian Staking.
Wrapped ABEL (wABEL) - wABEL is a QRC20 token on QDay that is 1:1 pegged to the ABEL coin on Abelian. It is used to bridge the ABEL token between the QDay Blockchain and the Abelian Blockchain. To mint wABEL, the user needs to lock the ABEL coin on Abelian and receive the corresponding amount of wABEL on QDay. To burn wABEL, the user needs to burn the wABEL on QDay and receive the corresponding amount of ABEL coin on Abelian. To support such operations, QDay team will implement an online service for the minting and burning of wABEL. The service will be operated by a union of institutions having Trust Service Provider (TSP) certification.
Abelian Staking - Abelian Staking is a dApp that enables users to stake ABEL on QDay in order to earn airdrop and staking rewards. The specific details of the airdrop and staking rewards will be announced at the launch of the QDay Mainnet.
Category 2: Legacy EVM-compatible Applications
Except for the first category, all dApps deployed in Phase 1 will function similarly to those on existing EVM-compatible chains. They will be compatible with legacy accounts and legacy wallets. To better support community-developed dApps, the QDay team will implement a set of fundamental DeFi dApps and make them available to the community at the launch of both the Testnet and the Mainnet.
QDay Bridge - QDay Bridge is a dApp to provide the cross-chain asset transfer functions. Unlike wABEL, QDay Bridge will focus on bridging ERC20, TRC20 and QRC20 tokens between QDay and other EVM-compatible chains.
QDay Swap - QDay Swap is a decentralized exchange (DEX) dApp to provide the token swap functions. To ensure QDay navigates the cold start period as smoothly as possible, the initial liquidity of QDAY, wABEL and the corresponding stable coins will be provided from the treasury of QDay and Abelian.
QDay Staking - QDay Staking is a dApp to provide staking functions for QDAY. Similar to Lido, staked QDAY will be used for the consensus mechanism of validators, and the rewards will be derived from validator rewards(see Tokenomics for more details).
QDay Lending - QDay Lending is a dApp to provide lending and borrowing functions for QRC20 tokens. It's similar to the lending protocols on the existing EVM-compatible chains such as Aave and Compound.
QDay Finance - QDay Finance is a consolidated dApp to integrate all the financial services including QDay Bridge, QDay Swap, QDay Staking, QDay Lending, etc. With the help of QDay Finance, the users can easily manage their DeFi assets and participate in various DeFi dApps in a unified interface.
Category 3: Quantum-Resistant Applications
QDay Phase 2, our focus will be on providing quantum-resistant versions of existing dApps. These dApps will serve as reference implementations of quantum-resistant contracts and dApps for the community. In addition, we will offer an external quantum-resistant signature generator to enable legacy wallets to interact with quantum-resistant contracts and dApps. Since Phase 2 is still in its early planning stages, further details about the quantum-resistant applications will be shared in the future.
7. Roadmap
The major milestones of QDay are shown below:
| Date | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 2024 Q2 | Start Phase 1 Development |
| 2024 Q3 | Launch of QDay Testnet |
| 2025 Q1 | Launch of QDay Mainnet and ABEL Staking |
| 2025 Q2 | Launch of QDay Finance dApps |
| 2025 Q3 | Start Phase 2 Development |
| 2026 Q2 | Major Upgrade of QDay Testnet for Phase 2 Upgrade |
| 2026 Q4 | Major Upgrade of QDay Mainnet for Phase 2 Upgrade |
To establish a strong foundation for the ecosystem following the TGE of the QDay Mainnet, the QDay team will focus on developing not only the blockchain technology but also essential ecosystem services and dApps. Below, we outline the detailed plans on a quarterly basis.
2024 Q2
Development of QDay Nodes - Implement all types of QDay nodes (validators, rollups nodes, etc.).
Development of ZK Rollups - Implement the ZK Rollups from QDay to Abelian.
2024 Q3
QDay Testnet (v1) - The first version of QDay Testnet is a POC (Proof of Concept) testnet to prove the feasibility of combining Rollups to Abelian with full EVM compatibility.
QDay Faucet (Testnet) - The QDay Faucet is a service to provide testnet tokens for the community including users and developers.
QDay Explorer (Testnet) - The QDay Explorer (Testnet) is a service to provide the blockchain data query and visualization functions for the QDay Testnet.
2024 Q4
QDay Testnet (v2) - The second version of QDay Testnet will be shipped with a comprehensive set of dApps and services to provide a full-fledged testing environment for the QDay ecosystem.
Testnet stable coins on QDay Testnet (v2) - The stable coins are essential for the QDay ecosystem. Testnet stable coins have no real value and are only used for testing purposes.
QDay Bridge (Testnet) - The QDay Bridge is a service to provide the cross-chain asset transfer functions. For the testnet, it only supports bridging stable coins between QDay Testnet and the testnet of a few selected public chains.
QDay Swap (Testnet) - The QDay Swap (Testnet) is a decentralized exchange (DEX) dApp to provide the token swap functions for the QDay Testnet.
QDay Staking (Testnet) - The QDay Staking is a service to provide the staking functions for QDay native tokens. The main purpose of the testnet staking is to test the staking, unstaking, and reward distribution processes for QDAY.
2025 Q1
EVM Compatibility - The QDay Mainnet will be fully EVM compatible.
Quantum-Resistant Rollups - The QDay Mainnet will conduct the rollups to the Abelian Mainnet.
QDAY Token Distribution - The QDAY token distribution will be conducted according to the tokenomics described in Section 3.
QDay Explorer - The QDay Explorer is a service to provide the blockchain data query and visualization functions for the QDay Mainnet.
QDay Bridge - The QDay Bridge is a service to provide the cross-chain asset transfer functions for the QDay Mainnet. For the mainnet, it supports bridging stable coins between QDay Mainnet and the mainnet of Tron and a rich set of EVM-compatible chains such as Ethereum, BSC, Polygon, etc.
QDay Swap - The QDay Swap is a decentralized exchange (DEX) dApp to provide the token swap functions for the QDay Mainnet.
QDay Staking - The QDay Staking is a dApp to provide the staking functions for QDay native tokens. On QDay Mainnet, most of the QDAY rewards will be distributed to the QDAY stakers and the validators.
Abelian Staking - The Abelian Staking is a service to provide the staking functions for Abelian native tokens.
2025 Q2
QDay Mainnet (Phase 1) - The QDay Mainnet (Phase 1) will be launched with the following features:
QDay Lending - The QDay Lending is a dApp to provide the lending and borrowing functions for QRC20 tokens.
QDay Finance - The QDay Finance is a consolidated dApp to integrate all the financial services including QDay Bridge, QDay Swap, QDay Staking, Abelian Staking, QDay Lending, etc.
2025 Q3
QDay NFT Marketplace - The QDay NFT Marketplace is a dApp to provide the NFT trading functions for the QDay Mainnet.
QDay Prediction Market - The QDay Prediction Market is a dApp to provide the prediction market functions for the QDay Mainnet.
Development of EVM compatible Quantum-Resistant Account - The first milestone of Phase 2 development is to implement the quantum-resistant account with full EVM compatibility.
2025 Q4
Development of QDay Wallet - The QDay Wallet is a new type of wallet to support the quantum-resistant account with full EVM compatibility.
Development of Quantum-Resistant dApps - The quantum-resistant dApps are upgraded from the legacy ones with the support of the quantum-resistant account.
2026 Q1
- Integration of Phase 2 technology - Consolidate the quantum-resistant account with the legacy one and conduct integration tests.
2026 Q2
QDay Testnet (Phase 2) - Launch the QDay Testnet (Phase 2) with the quantum-resistant account and QDay Wallet.
Quantum-Resistant dApps on QDay Testnet (Phase 2) - Launch the quantum-resistant dApps that can be used by the QDay Wallet on QDay Testnet (Phase 2).
2026 Q3
- Quantum-Resistant QDay Bridge (Testnet) - Launch the quantum-resistant QDay Bridge on QDay Testnet (Phase 2).
2026 Q4
QDay Mainnet (Phase 2) - Launch the QDay Mainnet (Phase 2) with the quantum-resistant account and QDay Wallet.
Quantum-Resistant dApps on QDay Mainnet (Phase 2) - Launch the quantum-resistant dApps that can be used by the QDay Wallet on QDay Mainnet (Phase 2).
Quantum-Resistant QDay Bridge (Mainnet) - Launch the quantum-resistant QDay Bridge on QDay Mainnet (Phase 2).
8. Conclusion
QDay represents a pioneering advancement in blockchain technology, offering the world's first quantum-resistant, EVM-compatible Layer 2 solution, built upon the trusted and proven foundation of the Abelian Blockchain. Through its visionary two-phase implementation strategy, QDay addresses the critical challenge presented by quantum computing while preserving the strengths of existing blockchain infrastructure.
Phase 1 establishes quantum-resistant ledger security through L1-assisted rollups, leveraging Abelian's quantum-resistant properties while preserving full EVM compatibility. The POS-over-POW consensus mechanism combines the security benefits of Proof of Work with the efficiency of Proof of Stake, creating a resilient security model. The integration of quantum-resistant rollups provides an extra layer of protection, enabling secure transaction processing and the ability to halt operations in response to detected threats.
Phase 2 advances quantum security at the account level, introducing quantum-resistant accounts, wallets, and smart contracts while maintaining backward compatibility with legacy systems. This thoughtful balance between innovation and compatibility ensures a smooth transition for existing users and developers, offering enhanced security features for those who need them.
QDay's comprehensive ecosystem approach, including key DeFi applications and cross-chain bridges, establishes a complete quantum-resistant blockchain environment. The platform's tokenomics model, featuring a well-balanced distribution strategy, ensures long-term sustainability while driving broad participation across the network.
Looking ahead, QDay's roadmap from 2024 to 2026 outlines a clear path toward full implementation, emphasizing thorough testing, gradual deployment, and ecosystem development. This methodical approach, combined with the platform's innovative technical features, positions QDay as a pioneer in quantum-resistant blockchain technology, equipped to address both current needs and future challenges in the evolving blockchain landscape.
By combining quantum resistance, scalability, and practical usability, QDay represents not just an incremental improvement, but a transformative leap in blockchain technology. It paves the way for a more secure and sustainable future for decentralized applications and digital assets.
9. References
[1] Abelian Official Website. https://www.pqabelian.xyz/
[2] Abelian Documentation. https://community.pqabelian.io/guide/
[3] Abelian Foundation. (2023, May). Post-Quantum Zero-Knowledge (PQZK) Bridge.https://download.pqabelian.io/release/docs/Abelian PQZK Bridge.pdf
[4] Abelian Whitepaper. https://community.pqabelian.io/guide/abel-whitepaper.html
[5] Abelian Foundation. (2025, Jan). Abelian Improvement Proposal 0011: Mnemonic Codes for Generating Deterministic Accounts. https://github.com/pqabelian/aips/tree/master/aips
[6] Fabian Vogelsteller, Vitalik Buterin. (2015, Nov). ERC-20: Token Standard. https://eips.ethereum.org/EIPS/eip-20
[7] Polygon zkRollup. https://docs.polygon.technology/cdk/concepts/zk-vs-optimistic/?h=polygon+zk+rollups#zero-knowledge-rollups
[8] Nakamoto, S. (2008). Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. https://bitcoin.org/bitcoin.pdf
[9] Wood, G. (2014). Ethereum: A Secure Decentralised Generalised Transaction Ledger. Ethereum Yellowpaper. https://ethereum.github.io/yellowpaper/paper.pdf
[10] Ethereum Foundation. ERC-20 Standards. https://ethereum.org/en/developers/docs/standards/tokens/erc-20/
[11] Ethereum Foundation. Decentralized Applications (dApps). https://ethereum.org/en/dapps/
Download the Japanese version of the QDay Whitepaper PDF document